

The rebirth of Applied Chemistry with a new name “Industrial Chemistry” was under the Department of Chemistry at Rangoon Arts and Science University in July 1967. Master’s study in Industrial Chemistry has been offering since 1974. It became a separate full-fledged department in March 1986. Industrial Chemistry integrates and applied knowledge within the disciplines of chemistry and chemical engineering.We can offer you hands-on learning experience in unit operations and unit processes with faculty dedicated in your learning process.Our mission is to conduct research related to Applied Science and transfer its important findings in the implementation and development of local on-going Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in Myanmar and to nurture graduates who would have better creativity and collaborative engagement and would possess improved and wider response in dealing with our local and regional communities. Vision of the department is to nurture and develop capacity and talents of students who will play an important role in the field of Applied Chemical Sciences and eventually become the main drivers for the sustainable development of the Applied Sciences-based Economic System.
Undergraduate Research
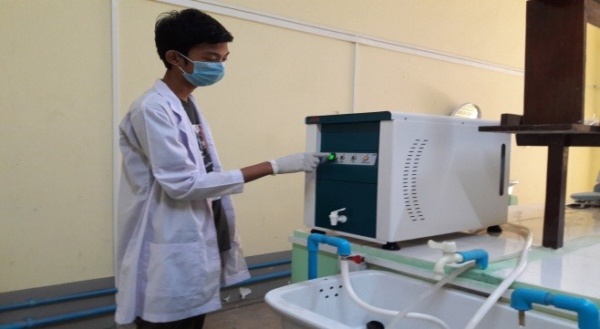


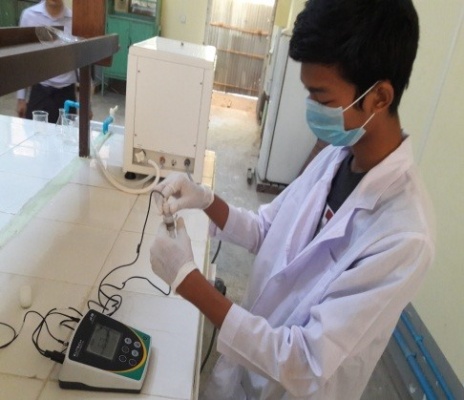
Department of Industrial Chemistry has practiced the students to take part in occasional field trips to plants and assign group project work with a submission of term paper at their final year of undergraduate studies. Currently, the department promotes the students’ interest on project work to growth of research interest. As the outcomes of growth interest in research, undergraduate students have received awards in national and international level project and research competitions. The department let students broaden their practical knowledge giving opportunities to access some instruments and special training for practical application of the basic concepts they learn in class.The contribution of the students’ scientific knowledge is encouraged by training their laboratory skills, capability of collect, analysis, evaluate, create and present the experimental results.
Graduate Research
Food Science and Processing Engineering
The sector of agro-based food processing is given priority to build up small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in Myanmar for her economic growth. The research program of the department is more emphasis on the areas of agricultural food processing, preservation and food safety that is nationally and internationally recognized cornerstone. Some food researches are urgently needed to respond to industry needs and solving food safety problems in Myanmar. Specific areas of food adulteration, food preservation, quality assessment, fermentation and study in browning during food processing, are placed on Master and PhD research.
Environmental Technology
Water quality is a very demanding subject and assessment of water quality for ground and surface water are focused on graduate research area. Good quality of finished product depends on the water quality. The department places its emphasis on quality analysis and treatment for potable purposes. A serious threat of large quantities of discharged effluents from industries may be an increase in environmental health concern. Research thus, focuses on conventional and biological treatment of wastewater to find out an appropriate method in place in industries. As regards in agricultural solid wastes, compositing and vermicompositing are focused on research areas of Master study.
Fuel Science and Renewable Energy
The comprehensive usage of coals available in Myanmar is focused on their proximate and ultimate analysis, and appropriate transformation of secondary fuel mixture like Coal-Water-Mixture. The renewable and nonfood competitive plant residues represent an abundant, inexpensive and readily available biomasses in Myanmar. With respect to availability of renewable biomasses, the utilization of energy from the biomass is considered as bioethanol processing. Research work on application of fruit wastes, waste fruits and lignocellulosic biomasses is emphasized for bioethanol production. In addition, biogas production from animal wastes and fish processing wastes was also included in graduate research.
Materials Science and Engineering
From the aspect of Industrial Chemistry, the materials science and engineering is to study on the manufacture of the new and the improvement of existing materials in chemistry, biochemistry, and electrochemistry. It ranges from basic concept within biology, physics and chemistry, to enabling technologies such as biotechnology, materials technology and nanotechnology. A variety of biomass-based materials also demonstrates key research themes in materials science and engineering, such as biofuel processing, biomass to hydrogen conversion, biochar based energy storage device, biochemical, biomass-based composites, and biopolymer-based composites. The energy derived from biomass using biomass conversion technology is only one form of renewable energy that can be utilized to reduce the high amount of energy demand and carbon emission. Thus, the researches of biomass conversion technologies and biomass-derived fuels/products including biodiesel production from used cooking oil, synergistically hydrothermal and biochemical treatment for the conversion of lingocellulosic biomass to ethanol, and biomass pellets are focused by Master and PhD candidates. The fabrication, properties and characterizations and, utilization of biomass based green composites and fiberboard also covers on the research of Master and PhD students.
Cosmetic Technology
Myanmar is rich in plant of fragrances and traditional natural cosmetics such as bark of thanakha plant, herbal shampoo made of fresh tayaw bark and soapnut (Kalakinmun) of are widely available. Quality and safe of traditional cosmetics are still in question. Convenient and safe cosmetic products are concerns to penetrate international market. In this regard, the department roots the research work on upgrading of convenient type of Myanmar traditional cosmetic products. Aside from that, extraction of natural dyes from plants and utilization in some cosmetic products, processing of medicated soaps and transparent soaps are placed as MSc research.
International Links and Project
The Department of Industrial Chemistry participates in international projects such as NutriSEA (Erasmus Projects 2016-18) and an Erasmus + 2018 project for capacity building of faculty members. The department is also networked with ASEAN universities and U.S. colleagues through regional conferences, workshops, SVAS (Short-term Visit Programme of AUN/SEED-Net), Fulbright programmes and hosting Fulbright specialists.
Field of Study
1. Food Science and Process Engineering
2. Fuel Science and Renewable Energy
3. Environmental Science and Engineering
4. Materials Science and Engineering
5. Chemical Technology
6. Biotechnology
7. Cosmetic Technology
8. Fats and Oil Technology
International Relations
Developing new BSc Curriculum in Industrial Chemistry with Professors from Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Advanced Science and Technology and Kyushu Institute of Technology
Dr Khin Swe Oo Professor
Dr Nwe Ni Win Professor
Dr Khin Si Win Professor
Dr Seinn Lei Lei Phyu Associate Professor
Dr Win Thi Yein Lecturer
Dr Nay Yee Nyunt Oo Lecturer
Undergraduate Studies
Core Courses of Bachelor of Science in Industrial Chemistry (Four-year Program, Total Credit Units 168)


* Elective courses
This is industrial chemsitry in yangon university.
# In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the Bachelor of Science in Industrial Chemistry degree, Fourth Year Students must take part in occasional field trips (to plants / factories) / project assignments, related to their field of studies, as deemed necessary by the Department of Industrial Chemistry and Submission of Term Paper at the end of the second semester.
First Year
Course Description
Industrial Chemistry I (Organic and Analytical Chemistry)
This module includes the structure and nomenclature of organic compounds and the fundamental principles of organic chemistry. It provides the basic concept of analytical chemistry and is also extended to acquire skills in various analytical techniques.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the fundamental principles and concepts related to Organic and Analytical Chemistry.
-Identify the organic compounds based on their functional groups.
-Apply these principles and concepts in the synthesis and processing of organic compounds.
-Analyze physical and chemical properties, methods of preparation, behavior of solutions and titration indicators.
-Solve the problems related to the calculation of acid base titration.
-Manipulate the Organic and Analytical experiments.
Industrial Chemistry II (Inorganic and Physical Chemistry)
This module provides concepts and principles in the synthesis and methods of processing. This unit deals with the study of different methods to analyze physical and chemical properties, behavior of gases, equilibrium constant. Moreover it can also study the operations and equipment for extraction of minerals and ores.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the fundamental principles and concepts related to basis chemistry of gases and liquids, colloids.
-Understand colloidal systems for industrial or technological interest.
-Analyze physical and chemical properties, behavior of gases, equilibrium constant.
-Manipulate the acid/base radicals and physical experiments.
-Identify the structure and configuration of atom, nature and energy of electron.
-Classify the position of metals and non-metals in the periodic table and their occurrence, extraction methods and application.
-Understand the methods of exploration, mining and concentrating of the ores, refining of metals and its processing.
Second Year
Course Description
Industrial Organic Chemistry I
This module aims to introduce the naming system, and physical and chemical properties of aromatic, heterocyclic compounds and natural products. This module includes the isolation techniques, preparation and physical and chemical properties of different types of industrially important derivatives.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the naming system of aromatic and heterocyclic compounds and their derivatives, the sources and pathways of preparation process.
-Apply the isolation techniques for extraction of alkaloids from plant materials.
-Categorize the physical and chemical properties of different types of carbohydrates, the preparation of different products (food and industrially important derivatives).
-Understand the types of amino acid and its nomenclature, physical and chemical properties, structure of amino acids and proteins.
Unit Operations I and II
This module aims to introduce industrial equipment for chemical processes, basic fluid dynamics and characteristics of different types of fluid flow. It provides the fundamentals of solid processing operation. This unit also involves fundamental principles and concepts related to calculation of mass and energy balances in heat exchangers, steam boilers and evaporators.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Operations I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand fundamental units, Dimensional Analysis, Process Development and Industrial Equipment for Chemical Processes.
-Understand the fundamental principles of flow of fluids, size separation, size reduction and sedimentation.
-Apply these mechanisms and principles in industrial engineering.
Unit Operations II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the fundamental principles and concepts related to calculation of heat balances.
-Apply these concepts and principles in the analysis of specified systems.
-Understand the mechanism of heat exchangers, steam boilers and evaporators.
-Analyze the material and energy balances in heat exchangers, boilers and evaporators.
Industrial Stoichiometry
This module aims to introduce chemical engineering calculations. This unit is also extended to the development of mass and energy balances as applied to the wide range of chemical processes such as distillation columns, evaporators and reactors.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the fundamental principles and concepts related to calculation of mass and heat balances in distillation and evaporation.
-Analyze the systems of heat transferred and mass transferred across the boundary.
-Derive the appropriate mass and energy balance equations for a giving system.
Learning Outcomes
Industrial Physical Chemistry I
This module deals with the basic concepts and criteria of thermodynamic, phase rule and catalysis. It also involves energy transfer for closed and control volume systems, the interpretation and application of binary phase diagrams and also the important of catalyst in a chemical reaction and their effects on reaction rate.
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the basic concepts of chemical thermodynamic such as temperature, pressure, system, properties, process, state, cycles, equilibrium, enthalpy and entropy.
-Understand the first law, second law and third law of thermodynamics.
-Know heat effect, thermodynamics properties of fluids and flow process.
-Understand the principles of binary phase diagrams.
-Interpret and apply the process conditions.
-Study the importance of catalyst in a chemical reaction and their effects on reaction rate.
-Apply thermodynamics concepts in analyzing the thermal efficiencies of heat engines such as Carnot cycles and the coefficients of performance for refrigerators.
Fuel Science and Technology
This module gives an overview of coal and petroleum industry. It includes the origins, types and qualities of coal and petroleum and their refining as well as introduction to biofuels.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the fundamental concepts, production, purification and combustion mechanism of fossil fuels (solid, liquid and gaseous).
-Classify the fuels according to their phase state as solid, liquid and gaseous and according to their properties.
-Apply the laboratory tests for the analysis of coal to assess its properties.
-Solve the problems related to combustion of fuel used in chemical process industries.
Third Year
Course Description
Water and Wastewater Technology I & II
This module aims to introduce the general knowledge of natural waters, water characteristics and treatment of water and wastewater. This unit also provides the natural water resources and water quality standards for boiler feed water, surface and ground water, and wastewater.
Learning Outcomes
Water and Wastewater Technology I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Identify the physical, chemical and biological parameters of the surface and ground water.
-Calculate the chemical parameters such as alkalinity and hardness.
-Recognize the water quality standards.
-Illustrate the fundamentals of water, boiler feed water and wastewater treatment.
-Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of softening and aeration.
-Gain knowledge on disinfection of water.
-Manipulate the experiments of water analysis.
Water and Wastewater Technology II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Describe and demonstrate basic knowledge of key principles underlying disinfection, coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation and filtration of water and wastewater.
-Describe the physical, chemical, and biological processes necessary for wastewater treatment processes.
-Understand the water pollution control.
-Apply the operational steps in water and wastewater treatment processes.
Unit Processes I & II
Main topics included are hydrolysis, esterification, oxidation, nitration, sulfonation and sulfation reactions in chemical process industries. This module deals with the principles, properties and application of various types of reagents and prime factors influencing the design of nitrators, and also possible side reactions during sulphonation.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Processes I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the process technologies of various organic and inorganic process industries.
-Describe the principles of oxidation, esterification and hydrolysis reactions in chemical process industries.
-Know the properties of various types of oxidizing gents, esterifying agents and hydrolyzing agents in chemical process industries.
-Apply the technology in manufacture of various inorganic and organic chemicals.
Unit Processes II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the principles of nitration, sulfonation and sulfation reactions involved in chemical process industries.
-Understand various types of nitration agents, sulfonating and sulfating agents.
-Analyze the pathway of the derivatives through the reactions.
Unit Operations I & II
This module gives an overview of mass transfer, phase equilibria, distillation, extraction and absorption. It involves the study of the fundamental principles of diffusion phenomenon and mass transfer. This unit also provides the equipment, different methods of computation and thermodynamic conditions related to the necessary experimental design.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Operations I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand mass transfer and diffusion in gas, liquid and solid molecules.
-Derive the equations to relate the necessary experimental data and the unknown phase conditions, temperature and pressure.
-Understand the separation techniques.
-Solve the problems related to distillation in chemical process industry.
Unit Operations II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to :
-Compare and contrast the concept of liquid-liquid extraction vs. solid-liquid extraction.
-Derive the mathematic equation of extraction processes.
-Solve the problems using the properties and relationships of extraction processes.
-Understand the mechanism of absorption process.
-Derive the mathematic equations for absorption process.
Industrial Physical Chemistry II & III
This module focuses on basic principles, concepts and mechanisms of chemical engineering kinetics and reactor design. It also provides on study of multiple phase reactions and reaction limitations in continuous and batch type reactors.
Learning Outcomes
Industrial Physical Chemistry II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Study the rate of chemical reactions and factors affecting the rate of chemical reaction.
-Understand reaction mechanism of chemical reactions.
-Classify the order of reaction and molecularity of chemical reactions.
-Apply various experimental techniques to measure the rate of a chemical reaction, order of reaction, rate constant, molecularity and activation energy in chemical process industries.
Industrial Physical Chemistry III
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the fundamental principles and concepts related to chemical reaction engineering and chemical kinetics.
-Apply these concepts and principles in the analysis of reaction systems.
-Analyze batch and continuous reactor system, multiphase reactor systems and their effects on the reaction.
Petrochemicals
This module gives an overview of the current and future technologies for the oil and gas industry. It involves the study of petrochemicals digest and their derivatives.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the sources of petrochemicals, techniques, skills and modern tools necessary for the processing of petrochemicals, synthetic gas and detergents.
-Categorize the key products and derivatives of petrochemicals in petroleum based industries.
-Understand the production routes of petroleum based industries.
Plastic Technology
This module gives an overview of the current and future technologies for plastic industry. It involves the study of the fundamental principles of plastic moulding techniques, modern plastic and general properties for design considerations.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the types and characteristics of raw materials in plastics industries.
-Know the types of plastics, plasticizers, fillers, resins and polymers.
-Understand the manufacturing and polymerization processes, molding techniques and the development of plastics products.
-Know the techniques for the production of elec¬tronic equipments, microelectronic devices and other industrial application.
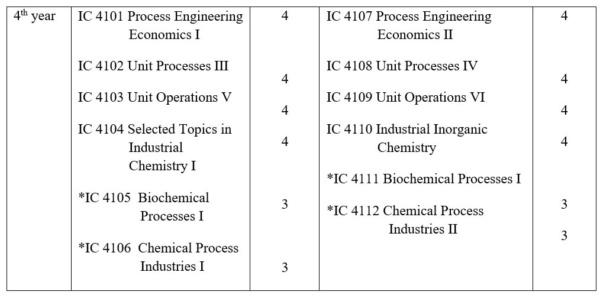
Fourth Year
Course Description
Process Engineering Economics I & II
This module aims to introduce plant design and economics analysis for chemical engineers. It involves the determination of optimum operating conditions in experimental design, cost estimation and industrial management. Moreover, the leadership and management skill can be taught in this module.
Learning Outcomes
Process Engineering Economics I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Analyze the optimum operating conditions for minimum cost of a process.
-Apply the concept of alternates based on the quantity or yields.
-Understand the cost estimation of an industry/ factory.
-Evaluate the economic feasibility of new processes and products.
Process engineering Economics II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the role of leadership and management of differences and conflicts.
-Understand complex ideas and tolerate ambiguity in managerial and organisational problem-solving.
-Understand the basic managerial decisions.
-Manipulate economic analysis for a selection of plant site.
Unit Processes III & IV
Mechanisms of hydrogenation, polymerization, alkylation and industrial polymerization practices can also be learnt in this module. Moreover, it can give the knowledge on the production and application of different resins, covering the alkylation and types of alkylation.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Processes III
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the principles and mechanism of hydrogenation and polymerization reactions involved in chemical process industries.
-Describe the importance of hydrogenation and polymerization catalysts.
-Analyze the techniques of hydrogenation in the production of various types of hydrogenated compounds.
-Apply the polymerization reactions in industrial processes.
Unit Processes IV
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the principles and mechanism of alkylation and polymerization reactions involved in chemical process industries.
-Know the types of alkylating agents in alkylation and catalysts of particular polymerization reactions.
-Apply the technical unit processes and principles of alkylation to produce alkyl aryl detergents.
-Understand industrial polymerization practices.
Unit Operations V & VI
This module gives an overview of filtration, crystallization, drying and their industrial applications. It also provides the empirical and fundamental tools in the design of the process and equipment.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Operations V
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand and apply the basic methods of crystallization.
-Evaluate efficiency and requirements of unit operations encountered in process engineering.
-Manipulate empirical and fundamental tools in the design of equipment and processes.
Unit Operations VI
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the basic concepts of drying and adsorption processes in each respective field.
-Know about the dryer types and their classification and operations.
-Study the mechanism of adsorption and types of adsorption, adsorbents and their uses.
-Apply the fundamental theory of adsorption of solid when contacting with fluid mixture and solve the problems encountered in chemical process industries.
Selected Topics in Industrial Chemistry I
This module includes the identification of industrial oil and fat products and also involves the description of their refining and production methods. Moreover, the student can learn the manufacturing processes and uses of soap and detergent, and nitrogen and nitrogen based products. As part of the module, the student can learn research methodology for contribution of research concepts, ideas, laboratory rules, academic writing format and style.
Learning Outcomes
Selected Topics in Industrial Chemistry I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand in the processing and analysis of fats and oils, soaps, detergents and fertilizer.
-Analyze the unit operations and processes involved in manufacturing.
-Understand the basic concept of research methodology, management process and laboratory housekeeping.
-Manipulate research systemically and effectively contribute to the community.
-Write an original/ good research/ project paper.
Industrial Inorganic Chemistry
This module aims to introduce the concepts and principles related to inorganic chemistry and nuclear chemistry. It provides limitations of composites materials used in chemical process industries, properties and uses of the nuclear fuel in nuclear power plants and fundamental concepts of corrosion and the related problems encountered in oil and gas industries.
Learning Outcomes
Industrial Inorganic Chemistry
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the main raw materials, production, properties and uses of composite materials
-Distinguish the types of matrices and reinforcement.
-Discuss the advantages and limitations of composites materials used in chemical process industries.
-Know the fundamental of radioactivity, radioactive decays and nuclear reaction.
-Identify the properties and uses of the nuclear fuel.
-Understand the nuclear reactor and nuclear power plants.
-Understand the fundamental concepts of corrosion and the related problems encountered in oil and gas industries.
-Apply the prevention and protection methods in the piping systems.
Chemical Process Industries I & II
This module can give an access to the factors influencing their manufacturing processes of inorganic acids, pulp and paper products, cosmetic products, and how to prevent the environmental effect related to the chemical industries.
Learning Outcomes
Chemical Process Industries I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the manufacture of the followings: chlorine and sodium hydroxide, sodium, sulphur, sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid, some inorganic chemicals, portland cement and glass.
-Identify the influencing factors for the manufacturing process of inorganic and organic products.
Chemical Process Industries II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the sources, conversion process and manufacture processes of pulp and paper products.
-Manipulate the conversion techniques from biomass into useful products.
-Understand the ingredients used in cosmetics and their functions.
-Describe the basic formulation of a cosmetic product.
-Manipulate the development of cosmetic product.
Undergraduate Studies
Core Courses of Bachelor of Science (Honours) in Industrial Chemistry (Five-year Program, Total Credit Units 216)

* Elective courses
# In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the Bachelor of Science (Honours) in Industrial Chemistry degree, Third Year Honours Students must take part in occasional field trips (to plants / factories) / project assignments, related to their field of studies, as deemed necessary by the Department of Industrial Chemistry and Submission of Term Paper at the end of the second semester.
First Year Honours
Course Description
Water and Wastewater Technology I & II
This module aims to introduce the general knowledge of natural waters, water characteristics and treatment of water and wastewater. This unit also provides the natural water resources and water quality standards for boiler feed water, surface and ground water, and wastewater.
Learning Outcomes
Water and Wastewater Technology I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Identify the physical, chemical and biological parameters of the surface and ground water.
-Calculate the chemical parameters such as alkalinity and hardness.
-Recognize the water quality standards.
-Illustrate the fundamentals of water, boiler feed water and wastewater treatment.
-Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of softening and aeration.
-Manipulate the experiments of water analysis.
Water and Wastewater Technology II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Describe and demonstrate basic knowledge of key principles underlying disinfection and wastewater treatment such as coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation and filtration.
-Understand the physical, chemical, and biological processes necessary for wastewater treatment processes.
-Understand the water pollution control.
-Apply the operational steps in water and wastewater treatment processes.
Unit Processes I & II
Main topics included are hydrolysis, esterification, oxidation, nitration, sulfonation and sulfation reactions in chemical process industries. This module deals with the principles, properties and application of various types of reagents and prime factors influencing the design of nitrators, and also possible side reactions during sulphonation.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Processes I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the process technologies of various organic and inorganic process industries.
-Describe the principles of oxidation, esterification and hydrolysis reactions in chemical process industries.
-Understand the properties of various types of oxidizing gents, esterifying agents and hydrolyzing agents in chemical process industries.
-Apply the technology in manufacture of various inorganic and organic chemicals.
Unit Processes II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the principles of nitration, sulfonation and sulfation reactions involved in chemical process industries.
-Understand various types of nitration agents, sulfonating and sulfating agents.
-Analyze the pathway of the derivatives through the reactions.
Unit Operations I & II
This module gives an overview of mass transfer, phase equilibria, distillation, extraction and absorption. It involves the study of the fundamental principles of diffusion phenomenon and mass transfer. This unit also provides the equipment, different methods of computation and thermodynamic conditions related to the necessary experimental design.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Operations I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand mass transfer and diffusion in gas, liquid and solid molecules.
-Derive the equations to relate the necessary experimental data and the unknown phase conditions, temperature and pressure.
-Understand the separation techniques.
-Solve the problems related to distillation in chemical process industry.
Unit Operations II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to :
-Compare and contrast the concept of liquid-liquid extraction vs. solid-liquid extraction.
-Derive the mathematic equation of extraction processes.
-Solve the problems using the properties and relationships of extraction processes.
-Understand the mechanism of absorption process.
-Derive the mathematic equation of absorption process.
Industrial Physical Chemistry II & III
This module focuses on basic principles, concepts and mechanisms of chemical engineering kinetics and reactor design. It also provides on study of multiple phase reactions and reaction limitations in continuous and batch type reactors.
Learning Outcomes
Industrial Physical Chemistry II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Study the rate of chemical reactions and factors affecting the rate of chemical reaction.
-Understand reaction mechanism of chemical reactions.
-Classify the order of reaction and molecularity of chemical reactions.
-Apply various experimental techniques to measure the rate of a chemical reaction, order of reaction, rate constant, molecularity and activation energy in chemical process industries.
Industrial Physical Chemistry III
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the fundamental principles and concepts related to chemical reaction engineering and chemical kinetics.
-Apply these concepts and principles in the analysis of reaction systems.
-Analyze batch and continuous reactor system, multiphase reactor systems and their effects on the reaction.
Petrochemicals
This module gives an overview of the current and future technologies for the oil and gas industry. It involves the study of petrochemicals digest and their derivatives.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the sources of petrochemicals, techniques, skills and modern tools necessary for the processing of petrochemicals, synthetic gas and detergents.
-Categorize the key products and derivatives of petrochemicals in petroleum based industries.
-Understand the production routes of petroleum based industries.
Plastic Technology
This module gives an overview of the current and future technologies for plastic industry. It involves the study of the fundamental principles of plastic moulding techniques, modern plastic and general properties for design considerations.
Learning Outcomes
Plastic Technology
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the types and characteristics of raw materials in plastics industries.
-Analyze the types of plastics, plasticizers, fillers, resins and polymers.
-Understand the manufacturing and polymerization processes, molding techniques and the development of plastics products.
-Know the techniques for the production of elec¬tronic equipments, microelectronic devices and other industrial application.
Second Year Honours
Course Description
Process Engineering Economics I & II
This module aims to introduce plant design and economics analysis for chemical engineers. It involves the determination of optimum operating conditions in experimental design, cost estimation and industrial management. Moreover, the leadership and management skill can be taught in this module.
Learning Outcomes
Process Engineering Economics I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Analyze the optimum operating conditions for minimum cost of a process.
-Apply the concept of alternates based on the quantity or yields.
-Understand the cost estimation of an industry/ factory.
-Evaluate the economic feasibility of new processes and products.
Process engineering Economics II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the role of leadership and management of differences and conflicts.
-Understand complex ideas and tolerate ambiguity in managerial and organisational problem-solving.
-Understand the basic managerial decisions.
-Manipulate economic analysis for a selection of plant site.
Unit Processes III & IV
Mechanisms of hydrogenation, polymerization, alkylation and industrial polymerization practices can also be learnt in this module. Moreover, it can give the knowledge on the production and application of different resins, covering the alkylation and types of alkylation.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Processes III
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the principles and mechanism of hydrogenation and polymerization reactions involved in chemical process industries.
-Describe the importance of catalysts in hydrogenation and polymerization.
-Analyze the techniques of hydrogenation in the production of various types of hydrogenated compounds.
-Apply the polymerization reactions in industrial processes.
Unit Processes IV
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the principles and mechanism of alkylation and polymerization reactions involved in chemical process industries.
-Understand the types of alkylating agents in alkylation and catalysts of particular polymerization reactions.
-Apply the technical unit processes of alkylation for alkyl aryl detergents.
-Understand industrial polymerization practices.
Unit Operations V & VI
This module gives an overview of filtration, crystallization, drying and their industrial applications. It also provides the empirical and fundamental tools in the design of the process and equipment.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Operations V
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand and apply the basic methods of crystallization.
-Evaluate efficiency and requirements of unit operations encountered in processes.
-Manipulate empirical and fundamental tools in the design of equipment and processes.
Unit Operations VI
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the basic concepts of drying and adsorption processes.
-Know about the dryer types and their classification and operations.
-Understand the mechanism of adsorption and types of adsorption, adsorbents and their uses.
-Apply the fundamental theory of adsorption of solid when contacting with fluid mixture and solve the problems encountered in chemical process industries.
Selected Topics in Industrial Chemistry I
This module includes the identification of industrial oil and fat products and also involves the description of their refining and production methods. Moreover, the student can learn the manufacturing processes of soap and detergent, and nitrogen and nitrogen based products. As part of the module, the student can learn research methodology for contribution of research concepts, ideas, laboratory rules, academic writing format and style.
Learning Outcomes
Selected Topics in Industrial Chemistry I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the processing and analysis of fats and oils, soaps, detergents and fertilizer.
-Analyze the unit operations and processes involved in manufacturing.
-Understand the research methodology, management process and laboratory housekeeping.
-Manipulate research systemically and effectively contribute data presentation.
-Write an original/ good research/ project paper.
Industrial Inorganic Chemistry
This module aims to introduce the concepts and principles related to inorganic chemistry and nuclear chemistry. It provides limitations of composites materials used in chemical process industries, properties and uses of the nuclear fuel in nuclear power plants. It also includes fundamental mechanism of corrosion and the related problems encountered in oil and gas industries.
Learning Outcomes
Industrial Inorganic Chemistry
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the main raw materials, production, properties and uses of composite materials
-Distinguish the types of matrices and reinforcement.
-Discuss the advantages and limitations of composites materials used in chemical process industries.
-Understand the fundamental of radioactivity, radioactive decays and nuclear reaction.
-Identify the properties and uses of the nuclear fuel.
-Understand the nuclear reactor and nuclear power plants.
-Understand the fundamental concepts of corrosion and the related problems encountered in oil and gas industries.
-Apply the prevention and protection methods in the piping systems.
Chemical Process Industries I & II
This module can give an access to the influencing factors on their manufacturing processes of inorganic acids, pulp and paper products, cosmetic products, and how to prevent the environmental effect related to the chemical industries.
Learning Outcomes
Chemical Process Industries I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
Understand the manufacture of chlorine and sodium hydroxide, sodium, sulphur, sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid, some inorganic chemicals, portland cement and glass.
-Identify the influencing factors in the manufacturing process of inorganic and organic products.
Chemical Process Industries II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the sources, conversion process and manufacture processes of pulp and paper products.
-Manipulate the conversion techniques for biomass into useful products.
-Understand the ingredients used in cosmetics and their functions.
-Manipulate and analyze the basic formulation of a cosmetic product.
-Manipulate the development of cosmetic products.
Third Year Honours
Course Description
Process Engineering Economics and Plant Design I & II
This module aims to introduce general design considerations, cost estimation related to optimum design, heat and mass transfer equipment design, handling and treatment of equipment for chemical engineers. It involves determining the optimum conditions of equipment as necessary in the plant design economically.
Learning Outcomes
Process Engineering Economics and Plant Design I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the equipment of many different units in the development of a complete plant design.
-Apply determining the optimum conditions in unit operations.
-Understand the costs, profits and the important factors in the design of industrial plants.
-Apply the engineering principles in the complete industrial plant design.
Process Engineering Economics and Plant Design II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the design and cost estimation of heat transfer and mass transfer equipment.
-Analyze the optimum conditions in heat transfer and mass transfer.
-Illustrate the optimum design of heat exchangers by applying basic theories of heat transfer.
Unit Processes V & VI
This module focuses on the mechanisms of amination, halogenation, hydrocarbon synthesis and hydroformylation. It also provides the Nano Science and Technology for the preparation of polymer additives, blends and polymer composites according to solid-state properties of polymers and fundamental thermodynamic relationships.
Learning Outcomes
Unit Processes V
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the solid-state properties of polymers, degradation and fundamental thermodynamic relationships.
-Understand the management of plastics in the environment.
-Understand the polymer additives, blends and polymer composites.
-Apply the nano particles in their related polymer science and technology fields.
Unit Processes VI
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the Fischer Tropsch synthesis processes.
-Understand the reduction methods by amination and halogenation process of the aromatic and aliphatic compounds.
-Understand the design and construction of the equipment for these processes.
Instrumental Methods of Analysis
This module gives the basic principles, instrumentation and applications of UV, IR and NMR spectroscopy. It also provides the identification and purification of organic compounds by interpreting UV, IR and NMR spectrums.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the basic principles and relevant terms of UV, IR and NMR Spectroscopy.
-Understand the instrumentation and working principle of UV, IR and NMR Spectroscopy devices.
-Interpret UV, IR and NMR spectrums for identification of organic compounds.
Unit Operations VII
This module gives an overview of chemical reactors, fluidization, industrial furnaces, dryers, and different industrial heating processes. This unit also provides the kinetics of homogeneous and heterogeneous reaction processes accompanied by their performance and design of these reactors and also the fuel economy measures and waste heat recovery in industrial furnaces.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the mechanisms of heterogeneous catalyzed and non-catalyzed reactions and importance of adsorption processes.
-Understand the rate expressions of heterogeneous reactions and catalysis.
-Solve the related problems with fixed bed and fluidized bed reactors.
-Evaluate the design of fixed bed and fluidized bed reactors for heterogeneous reactions.
-Design the component of operating conditions to optimize a desired product in chemical process industries.
Selected Topics in Industrial Chemistry II & III
This module aims to introduce the concepts and principles related to the food product industries, perfume and flavor industries, industrial gases and analysis. It involves the concepts of food processing, preservation and safety, extraction of fragrances from various sources and also the application and handlings of the most common industrial gases.
Learning Outcomes
Selected Topics in Industrial Chemistry II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the properties of major food constituents and of the biohazards with regard to product quality in food industry.
-Understand the awareness of the principles and importance of cleaning and sanitation in food process operations.
-Evaluate the food processing operations that can affect the quality of foods.
-Apply HACCP for food safety management to a food product design.
-Apply the technical knowledge of waste management in food industry.
Selected Topics in Industrial Chemistry III
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Apply the extraction methods of fragrances or essential oils from various plant sources.
-Understand the various constituents of perfumes and flavors.
-Apply the different synthetics and semi synthetics processes used in perfumes and flavors.
-Understand the industrial gases, specialty gases and its manufacture, uses and safety handling.
Fuel Science
This module includes the fundamental principles of energy conversion by the combustion process (solid fuels, liquid fuels and gaseous fuels) and energy conversion by nuclear reactions. It also provides management of radioactive wastes, application of renewable energy, biological fuel generation, fuel combustion calculation by applying the principles of energy conversion.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the characteristics of solids, liquid and gaseous fuels for the processing of secondary fuel mixture such as colloidal fuel, petroleum based hydraulic fluids, gasification, methane reforming and synthesis.
-Solve the problems related to the flammability characteristics of hydrocarbon and alcohols, chimney heights and maximum gas concentration at ground level in fuel science and technology.
-Illustrate the basic concept of techniques, skills and modern tools necessary for the processing of nuclear fuel, energy conversion by nuclear reaction and radiation hazards in fissile fuel.
Environmental Science
This module aims to introduce the basic principles underlying air water pollution, effect of weather on pollution, solid waste, chemical reaction in the atmosphere, and stratospheric ozone. This unit provides the water and air pollution prevention techniques in the environment and the management of solid waste, hazardous waste and pesticide.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the nature and types of water pollutants.
-Understand the reasons of water and air pollution from natural contaminants and various treatment methods employed for the removal of impurities.
-Understand the effects of air pollution on human and animals heaths.
-Evaluate the effect of weather conditions on influence of air pollution and climate changes.
-Apply the systematic use of pesticides and to minimize their impact on environments.
Process Biotechnology I & II
This module gives an overview of fermentation technology and industrial microbiology. It includes basic principles of microbiology, application of fermentation techniques using microorganisms in the processing of food and beverages, production of chemicals and antibiotics and also treatment of wastewater.
Learning Outcomes
Process Biotechnology I
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the growth of substances and environmental conditions required for microorganisms, microbial ecology, and bioreactors.
-Apply these concepts in the production of biomass as source of renewable energy, fermentation process for food production, waste water treatment and composting (will fermentation), production of alcoholic beverages from fruits and vegetables.
-Understand and manipulate the different fermentation processes, treatment of waste effluent from food industries.
-Analyze the effect of influencing factors on different fermentation processes,
Process Biotechnology II
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the basic concepts of biogas technology, production of energy and fertilizer on a decentralized basis for small farms.
-Understand the fermentation conditions.
-Understand the functions of different microorganisms in fermentation.
-Utilize fermentation technology in processing of food, beverages, antibiotics, amino acids, organic acids, and vitamins, etc.
-Understand the process of hydrogen production in biological system.
Courses in Master of Science (Two-year Program, Total Credit Units 64)
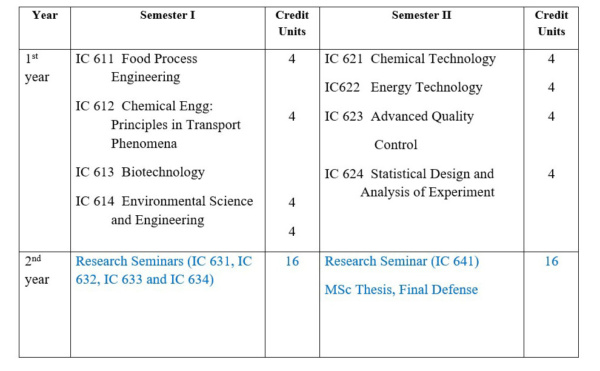
First Year MSc
Course Description
Food Process Engineering
This unit can provide the knowledge in the production of value-added fruits and vegetables related to agro-economics based on nutrition and food safety. Fats and oil technology and their physico-chemical properties are also included in this course.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand keeping the nutritional quality of fruits and vegetables, good quality of fats and oil.
-Apply the knowledge in production of value added fruits and vegetables related agro-foods.
-Integrate the production techniques by maximizing the yield and quality.
-Identify the operations involved in food processing industries.
-Analyze and evaluate the problems involved in unit operations.
Chemical Engineering Principles in Transports Phenomena
This module gives the principles and concepts related to phase separation including distillation and absorption. It also connected with the mass and heat transport phenomena when considering reactor design.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the phase separation in distillation and absorption units.
-Design proper separation techniques and heat and mass rates.
-Analyze the phases and heat and mass balances.
Biotechnology
The course deals with the metabolic pathway of carbohydrates, fatty acids and amino acids. It also involves principles of fermentation, bioremediation and wastewater treatment.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand advanced fermentation technology and various types of bioreactors.
-Understand the process layout of wastewater treatment.
-Understand the role of enzymes, their immobilization and productions.
-Understand about organic compounds and contaminants.
-Understand the Single-cell proteins and application of microorganisms in making foods.
Environmental Science and Engineering
Environmental Science and Engineering is the study of the principles of sustainable and green chemistry. Key topics are the characteristics of wastes from different industries and key concepts on waste disposal. It also illustrates the chemistry, toxicity, environmental fate and transport of twelve POPs.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the environmental and human toxicity of persistent organic pollutants.
-Understand the treatment methods of waste emerged from Industrial plant.
-Apply the systematic waste management system in chemical process industries.
-Identify the efficient methods of waste control in industrial plant.
-Illustrate the appropriate materials and methods used in control of environmental pollution problems.
Chemical Technology
This module focus on the production of ceramic, cement, glass, sugar and starch, pulp and paper, paint, varnish, lacquer and allied, leather, gelatin and glue products. It also covers the modern techniques for the preparation and applications of sulphur and nitrogen compounds.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the manufacturing process and quality control of sugar, starch and related products in sugar and starch industries.
-Understand the processing of paint, varnish, lacquer and allied in organic surface- coatings industries as well as processing, properties and uses of leather, gelatin and glue in leather and leather-tanning industries.
-Understand the fuel consumption in combustion of sulphur compounds, lime, cement and ceramic in chemical technology.
Energy Technology
This unit gives an overview of the current and future technology for deriving energy from biological resources. It also helps the students to understand both radiation and production of bioenergy and nuclear power.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Apply the processing technology for the production of bioenergy and biofuel (bioethanol, biodiesel) as renewable energy.
-Understand the radiation sources, effects of radiation and how to dispose radioactive waste.
-Review nucleon fusion and nuclear fusion power technology for the generation of nuclear power.
-Classify and analyze the lubricant oil blends which are designed to perform several jobs in engines and other industrial machines.
Advanced Quality Control
This course describes evaluation and interpretation of analytical data which eliminates probable error for sampling processes. It also includes the study of the HPLC and the performance of electrophoresis and electro-chromatography in addition to dealing with the principles of instrumental technique and isolating the elements in compound as pure a form as possible form as possible.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Manipulate the advance instrumentation of relevant terms of UV, IR, MS, NMR and AAS spectroscopy.
-Understand the instrumentation techniques and working principles of UV, IR, MS, NMR and AAS spectroscopy devices.
-Interpret UV, IR, MS, NMR and AAS spectrums for identification of organic compounds.
Statistical Design and Analysis of Experiments
This unit deals with the process design and experiment, using the basic statistics and statistical software. The process optimization, design and hypothesis of the experimental variables are covered in this unit.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the concepts related to sampling and population.
-Hypothesize the nature of research and experiments.
-Calculate and design the objective conclusion of data collected.
-Practice and demonstrate the research and experiment using statistics and statistical software.
-Verify the process design and process optimization.
-Relate the statistics in validation of research data.
-Manipulate the research skills using the statistical tool.
Courses in PhD in Industrial Chemistry (Five –year Program)

PhD Programme
Course Description
Energy Resource Technology
This module gives a board study of the energy conversion by combustion of solid, liquid and gaseous fuels. Key topics include power production, efficiency, operating principles of renewable energy production from various renewable sources.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the energy conversion by combustion of solid, liquid and gaseous fuels.
-Analyze the mechanism and chemistry of lubrication.
-Understand operating principles, power production, efficiency, energy yield of various renewable energy systems.
-Distinguish between the sustainable energy sources and fossil energy sources with emphasis on solar energy.
-Recognize the need of renewable energy technologies and their role in the Myanmar and world energy demand.
-Disseminate detailed technical aspect of fuel and energy technology.
Biotechnology
This unit let the students analyze chemical changes and biochemical processes and an emphasis will be placed on (1) preservation of the strain and purification of the strains and (2) manipulation of different fermentation states. Moreover, this also covers the concepts of bioreactors and membrane separation techniques.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the microorganisms, their growth and enzyme actions.
-Analyze chemical changes and biochemical processes.
-Integrate the preservation and purification of the strains.
-Manipulate different fermentation states.
-Adapt bioreactors and membrane separation.
-Integrate and practice fermentation processes.
-Identify different immobilization methods.
Food Science
This course deals with identification and classification of preserving techniques for particular foods. This unit delivers the message to the students about the important facts of temperature control in heat and cold preservation and also atmospheric control in preserving foods. This will investigate the manufacturing processes of various kinds of foods and their appropriate handling for food safety.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the temperature control in heat and cold preservation and atmospheric control in preserving foods.
-Analyze handling of foods and their constituents, hydrocolloids and manufacturing processes.
-Assess fatty acid profiles, refining of fats and oils focusing on soybean oil extraction and recovery of byproduct
-Adapt preserving techniques for particular foods and manipulate preservation methods.
-Manipulate appropriate food handling and manufacturing processes.
-Solve malpractices of food safety.
Environmental Science
This unit provides in-depth study on water and wastewater treatment, especially on advanced filtration technique based on the concepts of physical and chemical unit processes and operations. Moreover, this also focus on providing the students with the skills to understand the type and nature of air pollutants, the behavior of plumes and relevant meteorological determinants influencing the dispersion of air pollutants.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand in-depth knowledge of physical and chemical properties of unit processes and operations for water and wastewater treatment, especially on advanced filtration technique.
-Understand the radiobiological basis of radiation protection standards and effects radiation on environment and living things.
-Explain and use the main design criteria for water and wastewater treatment processes.
-Evaluate the health risks posed by abandoned toxic/hazardous waste sites and their waste disposal operations.
-Evaluate air quality management and analyze the causes and effects of air pollution.
-Disseminate detailed technical aspect of environmental engineering.
Courses in Diploma in Food Technology (One-year Program, Total Credit Units 32)
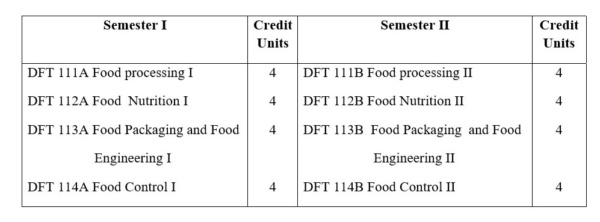
# In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of Post-diploma in Food Technology, Diploma Students must take part in occasional field trips (to plants / factories) / project assignments, related to their field of studies, as deemed necessary by the Department of Industrial Chemistry and Submission of Term Paper at the end of the second semester.
Course Description
Food Processing I and II
This module involves the study of sources of fats and oils, their properties and various processing methods as well as processing of milk and milk products, meat, fruits, vegetables, and manufacturing methods of fruit juice and beverages.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the sources and properties of fats and oils, milk and meat, fruits and vegetables and their various processing methods.
-Manipulate the products based on fats and oils such as butter, magarine, shortening, mayonnaise and salad dressing.
-Adapt to produce fruit juice, carbonated and non-carbonated beverages such as beer, wine, coffee and tea.
-Apply the milling, processing, fermentation techniques to manufacture of value-added cereal products such as bread, cornflakes and corn starch etc.
-Assess different preservation techniques of cereal and cereal products.
-Analyze the spoilage of cereals and cereal products, and range of fermentation processes.
Food Nutrition I and II
This course aims to provide knowledge in the nutritional value of food on the body as it relates to cholesterol, fat, salt and sugar intake. Knowledge of good nutrition that is vital for good health, disease prevention, and essential for healthy growth and development of children and adolescents is also achieved after this course.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the nutritional values of food on the body.
-Understand the requirements of good health, disease prevention, and essential for healthy growth and development of children and adolescents.
-Understand the structure and properties of biologic molecules.
-Understand the nutrition requirement for pregnant and lactating mothers and prevention of malnutrition.
-Synthesize the nutritive value and processing of supplementary foods, their preservation and function.
-Understand the handling and storage of foods with regard to their physico-chemical characteristics.
Food Packaging and Food Engineering I and II
This course introduces function of food packaging, classification of packaging and packaging containers in food industry and the testing methods of packages. After this course, students can be able to design the process plants and calculate the engineering problems related to mass and energy transfer.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the function of food packaging and primary materials used in packaging.
-Understand the type of packaging in food industry.
-Classify the types of packaging containers used in food industry.
-Perform the engineering calculations of process plant operations.
Food Control I and II
This course includes major topics of food deterioration and food-borne diseases. It also covers the fundamental principles and concepts related to food preservation by temperature control such as heat and cold processing, sanitary and hygienic practices and habits, national and international food regulations. This also covers the food safety, risks and hazard analysis.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, the students must be able to:
-Understand the major courses of food deterioration and food-borne diseases.
-Understand the principles of food preservation by temperature control.
-Analyze the food safety, risks, hazards and the effect of processing conditions on particular food.
-Apply the food preservation principles in the processing of fruits, vegetables and meat, food nutrition and labeling.
-Verify and solve the deterioration, risk and hazard of foods with the control of food safety.
-Integrate the concepts of food preservation, nutrition and labeling with governmental regulations.